Let us see, as to, what is Journal Entry? Its features, objectives, types, examples. It is the formal record of Business transactions in the books of accounts in chronological order complying with the accounting standards, rules of debit & credit, procedures, principles, policies. This has been explained in simple tactics below with the standard format and examples as well.
What is Journal Entry in Accounting? Its meaning, definition, features & format
Journal Entry is a formal record of all the business transactions that occur in any business entity. It is recorded in the daybook called Journal in chronological order(date wise). Journal is the primary book to record all business transactions. The entry made in the Journal is called Journal Entry. The process of recording all these transactions in a Journal is called Journalising.
Recording transactions in this daybook is the first step in Accounting Cycle. A Journal Entry is passed or booked as per the Golden rules of the Double-entry system. Each transaction is analysed as per the double-entry system and each transaction is classified as debit and credit. These transactions are recorded in the books of accounts following the debit and credit rules.
Under the Double Entry System of Accounting, all the business transactions are recorded as Debit and Credit. These are the two terms used in the Double entry system of accounting where both the aspects of business transactions are recorded as Debit and Credit. It means the business transactions are divided into two aspects as Debit and Credit. For every Debit, there is corresponding Credit. The sum of the Debit amount is equal to the Credit amount. The debit is receiving aspect and credit is the giving aspect and vice versa.
For example, John purchased goods from Rohan for $400.
Here, the purchase of goods is one aspect and is recorded as the Debit aspect. Cash is another aspect and is recorded as the Credit aspect. It is recorded as follows
Debit - Purchases $400
Credit - Rohan $400
Golden Rules of Double Entry System of Accounting are:
Personal Account:
Debit - The Receiver
Credit - The Giver
Real Account:
Debit - If an Asset comes into the business entity
Credit - If Asset goes out of the business entity
Nominal Account:
Debit - All expenses, Losses
Credit - All Incomes, Gains
Standard Format of Journal or Journal Entry:
Journal entry contains date, particulars, Ledger folio number, debit & credit amounts. It has 5 columns to record the transactions. It also gives the description of the transactions using Narration. The narration gives the summary or description of the recorded transaction. Thus each Journal entry contains five columns such as Date column, Particulars column, L.F as ledger folio column, Debit amount and Credit amount column. It is shown below as the standard format.
What are the different types of Journal Entries with examples?
There are mainly 9 different types of Journal entries in Accounting such as
1. Simple Entry
2. Compound Entry
3. Opening Entry
4. Closing Entry
5. Transfer Entry
6. Adjustment Entry
7. Rectifying Entry
8. Reversal Entry
9. Rebook Entry
Let us discuss each one to know as to what they are? how they are relevant in recording transactions of a business. Let see each one to know much more about them.
1. Simple Entry
Simple entries are those that have only two accounts. They have only one debit and one credit in it. Here, only two accounts are affected while recording transactions. One account is credited and the other is debited. For example, let us see this transaction. Robert sold goods for cash amounting to $1000. Here, we have two accounts where one account (cash) is debited and the other (sales) is credited.
Illustration for the transaction. Robert sold goods for cash amounting to $1000
Cash A/c - Debit $1000
Sales A/c - Credit $1000
2. Compound Entry
Compound Entries have more than two accounts that get affected while recording the business transactions.
Here, two accounts are credited and one account is debited. Even, two accounts may be debited or one account is credited. They are recorded for transactions that are similar in nature and occur on the same day.
Let us see the Illustration for this transaction. Paid salary $200, electricity bill $100, rent $300.
Salary A/c - Debit $200
Electricity A/c - Debit $100
Rent A/c - Debit $300
Cash A/c - Credit $600
3. Opening Entry
These are used to record the balances of assets, liabilities, capital, reserves & surplus that are brought forward from the previous year. All the closing balances of assets, liabilities, capital that are shown in the last years' balance sheet are brought forward to the current year using this opening entry. We generally use, "To balance b/d", "By balance b/d" as the transaction type to record these opening balances of assets and liabilities
4. Closing Entry
These are used to close the balances of revenues A/c, incomes A/c, expenses A/c. Generally, all the nominal accounts are closed and transferred to the Trading, Profit & loss account at the end of the financial year. All the incomes & expenses such as sales A/c, incomes earned, rent A/c, salary A/c will be closed and transferred to the Trading A/c, Profit and loss A/c. These expenses and incomes are closed and not carried forward to the next financial year.
5. Transfer Entry
These are used to transfer the amount in one account to another account. They are used, when a wrong booking was made, where a wrong account has been credited or debited. In such a case, such amounts will be transferred to the correct account.
6. Adjustment Entry
They are used to record the assets and liabilities at their correct value. It means they are used to adjust the assets, liabilities, incomes, expenses while preparing the financial statements at the year-end. For example, depreciation is used to show the assets at their true value. Depreciation is calculated and deducted from the assets book value to show its correct value in the balance sheet. Provision for bad and doubtful debts are deducted from the debtors' balance in the balance sheet to show its true balance.
7. Rectifying Entry
They are passed to make corrections in the books of accounts, ledger accounts. Whenever errors take place while booking the transactions in the books of accounts, we will pass rectifying entries to correct them. Errors may be of many types such as error of commission, principal errors, error of omission, compensating errors.
8. Reversal Entry
This is used to reverse any transaction originally booked. This is to nullify the effect of that wrong transaction booked earlier. Thus it would be helpful to reverse any transaction booked wrongly in the books.
Then we will pass Rebook entry to book the transaction correctly in the books.
9. Rebook Entry
This is used to reverse any transaction originally booked. This is to nullify the effect of that wrong transaction booked earlier. Thus it would be helpful to reverse any transaction booked wrongly in the books.
Then we will pass Rebook entry to book the transaction correctly in the books.
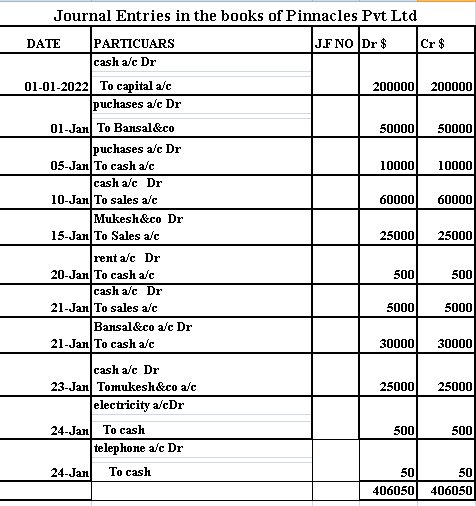
Illustration 1: Journalise the following transactions in the books of Pinnacles Pvt ltd:
1 Jan 2020, business started with cash 200000 $
1 Jan, goods purchased from Bansal &co worth 50000$
5 Jan, cash purchases worth 10000$
10 Jan, cash sales worth 60000$
15 Jan, sales to Mukesh &co worth 25000$ on credit
20 Jan, paid rent 500$
21 Jan, cash sales 5000$
21 jan, paid to bansal&co 30000$
23 Jan, received cash from mukesh&co 25000$
24 Jan, paid electricity bill 500$
24 Jan, paid telephone bill 50$
Let us look into the solution of the above transactions in a standard format as well.
In the above example, all the journal entries are booked by complying with the Golden rules of the Double-entry system. If we analyse the above journal entries we notice that each journal entry has two accounts where one account is debited and another account is credited. Every Transaction has two accounts with debit and credit. This is because of the double-entry system of bookkeeping which is a logical and scientific method of recording financial transactions in books of accounts.
Conclusion:
It has been explained, as to, what is a journal entry in accounting? Also, its meaning, features, objectives, types, format with examples have been explained in a simple tactic. Thus, we conclude that Journal entry is a formal record of all business transactions that occur in any business organisation. It is recorded as per the golden rules of the double-entry system using debit & credit rules.
Related blogs:
What are Ledgers?
What is Trial Balance?
What are Financial Statements? Its features, types, uses
What is Income Statement (Profit and loss a/c)?
What is Balance Sheet (Position Statement)?
What is Cash Flow Statement?
What is Bookkeeping? Its features, objectives, uses?
What are Subsidiary Books? Its features, types, objectives, uses
What is Single Entry System? Its features, types, objectives, uses
What is Double Entry System? Its features, objectives, uses



Post a Comment
if you have queries let me know and mail me at syednissaruddin99@gmail.com