Let us see, as to, What is Journal in Accounting? Its features, objectives, types, uses. Also, see how it would help us to know the relevance, scope and uses of this daybook in recording day to day business transactions.
What is Journal in Accounting? Its meaning, definition, nature & scope:
It is the book of primary entry where the business transactions are recorded primarily in this book. The entry made in this book is called a journal entry. All the business transactions are first recorded in this book in chronological order or date wise. It is the book of original entry where the business transactions are recorded in a format of debit and credit.
Journalising: All the business transactions are recorded in this book in chronological order. The process of recording transactions in the journal is called journalising. The transactions are recorded in this book as per the double-entry system of accounting which has dual aspect such as debit aspect and credit aspect.
Sources of documents: At first the transaction takes place in business such as purchase of goods and services for cash or credit. The supplier or merchant issues invoice or cash memo or receipt for purchase of goods. The business entity issues sales invoice or cash memo for cash or credit sales made to customers. These sales or purchase invoice are called sources of documents. These sources of documents are the basis for passing the journal entries in the journal.
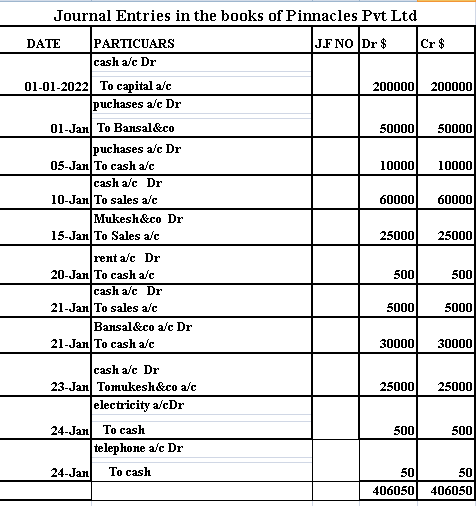
Illustration 1: Journalise the following transactions in the books of Pinnacles Pvt ltd:
1 Jan 2020 business started with cash 200000 $
1 Jan goods purchased from Bansal &co worth 50000$
5 Jan cash purchases worth 10000$
10 Jan cash sales worth 60000$
15 Jan sales to Mukesh &co worth 25000$ on credit
20 Jan paid rent 500$
21 Jan cash sales 5000$
21 jan paid to bansal&co 30000$
23 Jan received cash from mukesh&co 25000$
24 Jan paid electricity bill 500$
24 Jan paid telephone bill 50$
Let us look into the solution of the above transactions in a standard format as well.
In the above example, all the journal entries are booked by complying with the Golden rules of the Double-entry system. If we analyse the above journal entries we notice that each journal entry has two accounts where one account is debited and another account is credited. Every Transaction has two accounts with debit and credit. This is because of the double-entry system of bookkeeping which is a logical and scientific method of recording financial transactions in books of accounts.
What are the main objectives ( purpose) of Journal in Accounting?
1.
The main objective is to record all the business transactions in chronological order or date wise. The first & foremost important objective of the Journal is recording all the financial transactions that occur in a business entity. All transactions that occur in any business are recorded in this daybook on daily basis in chronological order or date wise. Each transaction is recorded using
the double-entry system of
bookkeeping. Narration is used to explain the description or nature of the transaction in each entry.
2. Journal is the legal evidence that all the business transactions are recorded and required books of accounts have been maintained as per the legal requirements of the various laws. Maintaining this daybook implies that a business entity complies with the legal requirements and various laws of the state as well.
3.
The basic purpose of preparing the Journal is to facilitate the preparation of the Ledger. A ledger is a bound book that contains all the relevant ledger accounts of debtors, suppliers, expenses, incomes, liabilities, assets, capital. Each ledger account has T shape where the left side is denoted as Dr (debit) and the right side as Cr (credit). All these
ledgers accounts are balanced where all these balances are taken to
trial balance and
financial statements. Thus, it also helps in the preparation of
Leger.
4. Journal gives the complete information of all the transactions that occurred in the business. All the transactions are accounted for and recorded in a systematic manner. We have supports, documents, invoices, bills for all the transactions that occurred in the business. We also use Narration for each transaction recorded as an explanation to the transaction.
5.
The main purpose of preparing a Journal is to show that all the transactions are recorded by complying with the golden rules of the double-entry system of bookkeeping. This implies that all the transactions are recorded using a systematic and logical method of bookkeeping called the double-entry system. Under the
Double Entry System of Accounting, all the
business transactions are recorded as
Debit and
Credit. These are the two terms used as Debit and Credit. It means the business transactions are divided into two aspects as Debit and Credit. For every Debit, there is corresponding Credit. The sum of the Debit amount is equal to the Credit amount. The debit is receiving aspect and credit is the giving aspect and vice versa
what are the characteristic features of Journal in accounting?
1. The Book of Original entry or Primary entry
It is the book of original entry or primary entry because the transactions are first recorded in this daybook. All the transactions are identified, analysed and recorded in this book. Transactions are recorded as per the
Golden rules of the double-entry system. Debit and credit analysis is done to record the transactions. Each transaction is divided into debit and credit to record by giving narration as an explanation to it.
2. Transactions recorded in Chronological order or date wise
All the transactions are recorded in chronological order. It means they are recorded date wise. Hence, all the transactions will be booked in this daybook, following the date pattern. For example, goods sold on 1 January will be recorded first and goods sold on 2 January will be recorded second to it. Goods sold on 3 January will be recorded next to it. In this way, the transactions are recorded in chronological order meaning date wise.
3. Narration gives the complete information of the transaction
Narration is a brief explanation of the transaction recorded in this daybook. Narration is used while recording transactions to know the information of that particular transaction. For example, goods sold to John for $1000 on credit. Now, the narration would be as follows - " Being goods sold to John for $1000". This narration helps to identify the nature & type of the transaction recorded. The narration also helps to get the complete information on that particular transaction
4. Complies with the Golden rules of the Double-entry system
Transactions are recorded as per the Golden rules of the double-entry system. Debit and credit analysis is done to record the transactions. Each transaction is divided into debit and credit to record by giving narration as an explanation to it. For example, goods sold to John for $1000 on credit. This transaction would be recorded as per the Golden rules of the double-entry system as follows: Debit - John $1000
Credit- Sales $1000
Here, John was debited for $1000 as he is a debtor and owes money to the business entity for $1000. Sales are being credited as the business made sales for $1000.
5. Different types of Journal
There are different types of day books. Such as General Journal and
Subsidiary Journal. This classification is done to avoid repetitive work where the volume of transactions is high. This classification also helps to record transactions in a smooth and efficient manner by avoiding clerical work. This also helps to avoid errors and mistakes while recording a large number of transactions in big organizations.
6. The book has five columns with standard format
This book of primary entry has a standard format with five columns to record the transactions. There are five columns which include the date column, particulars column, Ledger folio column, debit amount column and credit amount column. Finally, the debit amount and credit amount columns must be equal after making totals.
7. It contains different types of Journal entries
There are
different types of entries while recording transactions. This is to make the recording easy and smooth. Different types of entries would include compound entry, simple entry, opening entry, closing entry, adjustment entries, transfer entries, rectifying entries. For example, the simple entry has two-fold aspects such as the debit and credit aspect. There is only debit and one credit under simple entry. But there are more than one debit or credit under compound entry. Opening and closing entries are to open or close the transaction recording. Whereas adjustment entries or rectifying entries are made to rectify or adjust the entries.
8. It is also called the Daybook or Subsidiary book to record day to day transactions
This book is also called the daybook or
subsidiary book to record a large number of transactions in big organisations. In case of big business concerns, Journal is classified into different books called
subsidiary books to record a large number of transactions. For example, we have different subsidiary book such as purchase book, sales book, purchase return book, sales return book, Cashbook, bills receivable book, bills payable book, Journal Proper. These subsidiary books make the record-keeping work smooth, easy, efficient.
9. Assistance to Ledger
It means, this daybook helps to prepare the Ledger.
Ledger is a book of secondary entry to record the transactions in different accounts in T shape or format. After recording transactions in this daybook, these transactions are transferred to Ledger. This process is called
Ledger Posting.
10. Journalizing is the process to record transactions in Journal
As we already discussed, it is the process to record the transactions in this daybook. This is the first process of recording transactions in this daybook. This process helps to record the transactions as per the golden rules of the double-entry system using a standard format. The transactions are recorded using narration to give an explanation to each transaction.
What are the 10 different types of Journal in Accounting?
In the case of small organisations such as sole trading concerns, we generally maintain
General Journal to record a few transactions. However, in case of big business concerns, we will divide this Journal into
Special Journal to record a large number of transactions depending upon the nature, type of transaction. In case of big business concerns, these books are also called
Subsidiary Books. For example, to record credit purchase of goods we have a Purchase book. To record credit sale of goods, we use Sales book. Similarly, we have purchase return book and sales return book to record return inwards and return outwards. To record cash purchases and cash sales, we have a cash book. We have bills receivable & payable book to record transactions relating to bills received and issued. All other transactions such as opening entries, closing entries, adjustment entries, rectifying entries are recorded in Journal Proper.
1. General Journal
In case of small business concerns, they maintain General Journal, to record all the transactions in this book. Since the volume of transactions is pretty low, they can go with this daybook, to record all the transactions in this one book. This sort of daybook is suitable for small and medium-sized business concerns to record all the business transactions, post them to the ledger and prepare financial statements at the end of the year.
2. Purchase Journal
This daybook is maintained by big business concerns to record the credit purchase of goods & services. This daybook is used only to record the purchase of goods on credit from suppliers. We can find only credit purchase of goods recorded in this daybook. This is also called purchase daybook For example, purchased goods from David for $1000 on credit will be recorded in this purchase daybook.
3. Sales Journal
This daybook is maintained by big business concerns to record the credit sale of goods & services. This daybook is used only to record the sale of goods on credit to customers. We can find only credit sale of goods recorded in this daybook. This is also called sales daybook. For example, sold goods to John for $1000 on credit will be recorded in this sales daybook.
4. Purchase return book
This book records the purchase return of goods that are originally purchased on credit from suppliers. This daybook is also called return outwards book
5. Sales return book
This book records the sales return of goods that are originally sold to customers on credit. This daybook is also called return inwards book
6. Cash receipts Journal
All the transactions which involve cash receipts to the business firm will be recorded in this daybook. For example, receipt of cash from customers on account of goods sold, receipt of cash on account of machinery sold will be recorded in this Cash receipts daybook.
7. Cash payments Journal
All the transactions which involve cash payments made by the business firm will be recorded in this daybook. For example, cash paid to suppliers on account of purchases made, purchase of machinery for cash will be recorded in this Cash payment daybook.
8. Bills receivable Journal
This book records transactions relating to the bills receivable that are drawn in favour of the business firms. All the bills which are drawn in favour of the business firm will be recorded in this Bills receivable book
9. Bills payable Journal
This book records transactions relating to the bills that are payable by the business firm. All the bills which are payable by the business firm will be recorded in this Bills payable book
10. Journal proper
This book records the transactions that are not recorded in any of the above daybooks. For example, transactions relating to credit purchase of fixed assets and sale of assets on credit will be recorded in this daybook. Opening entries, closing entries, adjustment entries, rectifying entries are also recorded in this daybook
Conclusion
The above discussion and clarification help us to know, what is Journal in Accounting? Its features, objectives, types, uses as well. This detailed discussion helps us to know the relevance and scope of this daybook as the primary book to record the business transactions in the business organisation.
Related Blogs:
What are Subsidiary Books? Its features, objectives, uses
What is Bookkeeping?
What is the difference between Bookkeeping and Accounting?
What is Accounting Cycle? What are the 10 steps of the Accounting Cycle?
What is a Single Entry System? Its features, objectives, types
What is the Double Entry System?
What are Ledgers?
What is Trial Balance?


Post a Comment
if you have queries let me know and mail me at syednissaruddin99@gmail.com